

PricewaterhouseCoopers(PwC), is a multinational professional services network known for its extensive range of services, including assurance, advisory, and tax consultancy. The company is one of the "Big Four" accounting firms and has a strong reputation for working with some of the world's most influential businesses and governments. PwC operates in over 150 countries, employing more than 300,000 professionals globally. PwC is highly regarded for providing high-quality services and solutions, driving its clients' growth and success across various industries.
This blog is a comprehensive guide, offering detailed insights into PwC’s history, its business operations, key services, and career opportunities for students preparing for interviews with the company. With a focus on developing leadership and problem-solving skills, PwC presents a platform for ambitious individuals looking to make a mark in the consulting and professional services domain.
1. PwC Overview
About
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Founder | Samuel Lowell Price, William Cooper, and Others |
| Industry Type | Professional Services (Audit, Assurance, Consulting, and Tax) |
| Founded | 1849 (Price), 1854 (Cooper) |
| Headquarters | London, UK |
Company History
PwC’s history is a tale of mergers, global expansion, and industry leadership:
Founding and Early Years (1849-1920s)
- 1849: Samuel Lowell Price establishes an accounting practice in London, which later becomes Price Waterhouse.
- 1854: William Cooper opens his own practice, leading to the formation of Cooper Brothers.
- 1920s: Both firms expand globally, setting up offices in the United States and other countries.
Mergers and Expansion (1950s-1998)
- 1957: Price Waterhouse and Cooper Brothers, along with other firms, create the “Big Eight” accounting firms.
- 1998: Price Waterhouse and Coopers & Lybrand merge to form PricewaterhouseCoopers, creating one of the largest professional services networks in the world.
Globalization and Modernization (2000s-Present)
- 2002: PwC divests its consulting arm to IBM, refocusing on audit and tax services.
- 2010s: PwC reintroduces consulting services, rapidly expanding in the areas of digital transformation and cybersecurity.
- 2020s: PwC continues to lead in innovation, focusing on ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) services and digital trust.
Key Milestones in PwC's History
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1849 | Samuel Lowell Price establishes the firm in London. |
| 1854 | William Cooper starts Cooper Brothers, a foundation of PwC’s lineage. |
| 1998 | Merger of Price Waterhouse and Coopers & Lybrand forms PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC). |
| 2002 | Divestiture of PwC’s consulting arm to IBM, refocusing on core audit and tax services. |
| 2010 | Reintroduction of consulting services, with a focus on digital transformation and innovation. |
| 2021 | PwC launches "The New Equation," a strategy focusing on building trust and delivering sustained outcomes. |
2. Company Culture and Values
Mission
PwC’s mission emphasizes its commitment to integrity and ethical business practices, striving to make a positive impact on society by addressing complex business challenges.
Vision
PwC aims to maintain its leadership in professional services by continuously evolving to meet the changing needs of clients and society.
Core Values
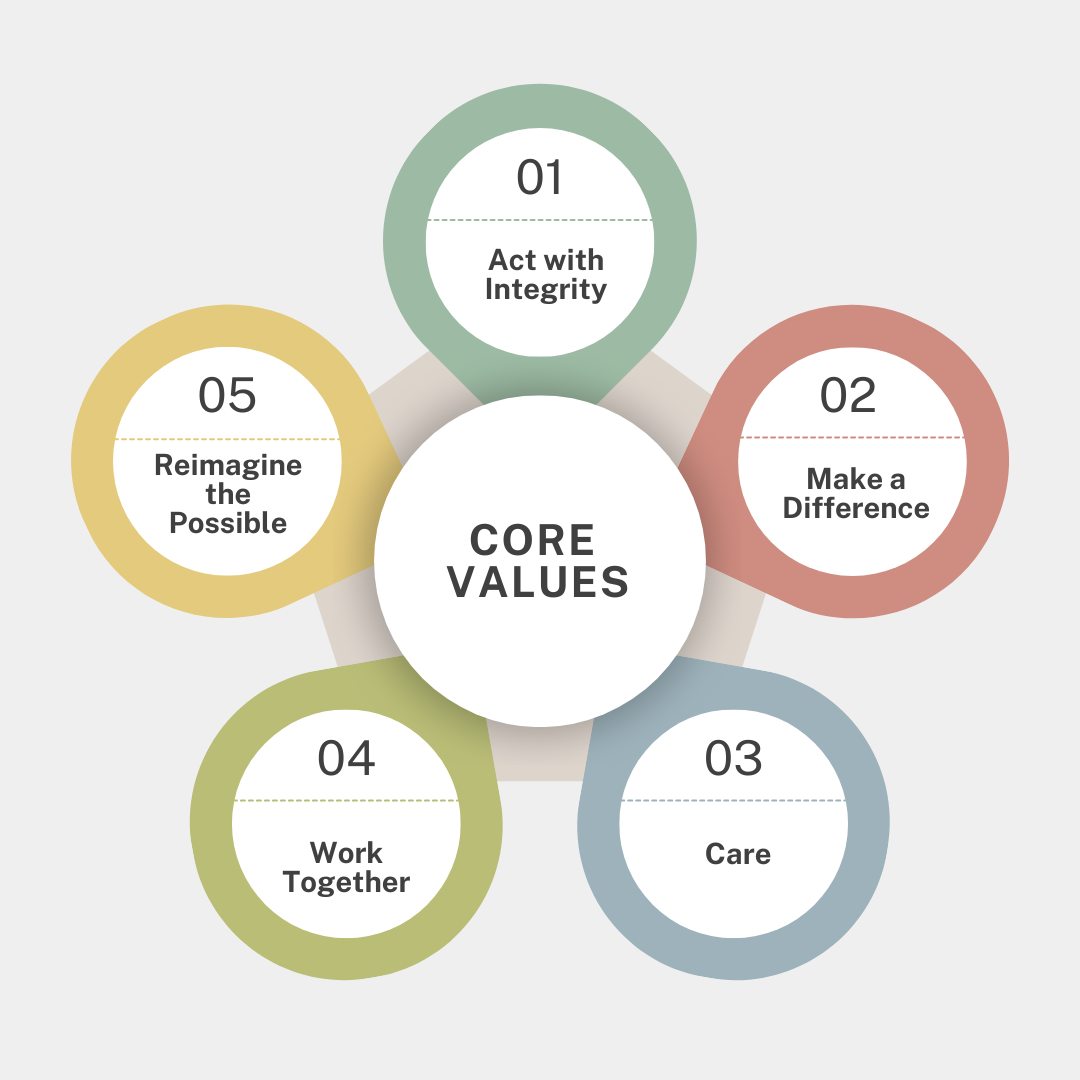
- Act with Integrity: Upholding the highest ethical standards in all interactions.
- Make a Difference: Delivering high-quality work that positively impacts clients and society.
- Care: Fostering a culture of respect, inclusion, and well-being.
- Work Together: Emphasizing collaboration and collective success.
- Reimagine the Possible: Encouraging innovation and embracing change.
Code of Conduct
This Code emphasizes our commitment to integrity and trust in all professional interactions. It encourages speaking up about concerns, maintaining high standards, protecting confidential information, and fostering respectful relationships. By following these principles, we uphold our reputation and create a positive impact in our workplace.

3. Comprehensive Product and Service Offerings
PwC provides integrated professional services spanning assurance, consulting, tax and legal, deals, and risk. The firm combines deep sector expertise with technology-enabled solutions, covering areas such as ESG reporting, cloud transformation, cybersecurity, data and analytics, and complex transactions to help clients build trust and deliver sustained outcomes.
1.Assurance (Audit & Assurance)
PwC’s assurance services enhance confidence in financial and non-financial information, underpinned by rigorous methodologies, independence standards, and evolving digital audit tools.
- Financial Statement Audit: Independent audits of financial statements in accordance with applicable standards, providing stakeholders with reliable, decision-useful information.
- Sustainability/ESG Reporting Assurance: Assurance over sustainability and ESG disclosures, including climate and non-financial reporting frameworks, to build trust in reported impacts and metrics.
- Internal Controls and SOX Services: Advisory and attestation services on internal control over financial reporting and related regulatory requirements.
2.Consulting
PwC Consulting helps organizations transform strategy, operations, and technology bringing together capabilities from Strategy& (strategy consulting) through execution, supported by cloud, data, and digital platforms.
- Strategy&: PwC’s strategy consulting business that partners with leaders on corporate, business unit, and capability strategies, from vision to realized results.
- Cloud and Digital Transformation: Design and delivery of cloud-enabled operating models and modern platforms to improve agility, scalability, and customer experience.
- Cybersecurity and Privacy: End-to-end cyber strategy, threat detection and response, identity, data protection, and privacy programs aligned to regulatory requirements.
3.Tax and Legal Services
PwC provides tax compliance, reporting, and advisory services, alongside legal business solutions in many territories, helping organizations navigate complex, cross-border rules and create tax-effective, compliant structures.
- Corporate Tax Compliance and Reporting: Preparation and review of tax filings, provision calculations, and reporting processes across jurisdictions.
- Transfer Pricing: Design, documentation, and dispute support for intercompany pricing aligned with OECD and local regulations.
- People and Organisation (Global Mobility): Advisory on employment taxes, mobility, rewards, and immigration to manage a global workforce effectively.
4.Deals
PwC’s Deals practice supports the transaction lifecycle strategy, diligence, valuation, and integration/divestiture helping buyers, sellers, and investors create and protect value.
- Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A) Advisory: End-to-end support for acquisitions, divestitures, and joint ventures, including deal strategy and execution.
- Transaction Diligence: Financial, tax, commercial, and operational due diligence to assess risks and confirm value drivers.
- Valuations and Business Modelling: Independent valuations and analytical models for transactions, financial reporting, and strategic decision-making.
5.Risk Services
PwC helps organizations anticipate, manage, and monitor risk across governance, compliance, operations, technology, and third parties, aligning risk management to strategy.
- Risk Assurance and Internal Audit: Independent risk and controls assessments, internal audit co/outsourcing, and reporting to boards and audit committees.
- Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC): Framework design and implementation for regulatory compliance, enterprise risk management, and controls automation.
- Forensic Services and Investigations: Investigations, dispute advisory, and forensic technology services to prevent, detect, and respond to misconduct and economic crime.
4. Key Competitors of PwC
PwC operates in a competitive landscape with several key players in the professional services sector. Here are the top competitors:
1. Deloitte
- Overview: Deloitte, founded in 1845, is one of the "Big Four" professional services firms, offering audit, consulting, tax, risk management, and financial advisory services.
- Services: Deloitte provides services in areas such as audit and assurance, consulting, financial advisory, risk management, and tax.
- Market Position: Deloitte is a direct competitor to PwC, particularly in audit, tax, and consulting services. Both firms compete globally across a wide range of industries and sectors, with a strong focus on innovation and digital transformation.
2. EY (Ernst & Young)
- Overview: EY, another of the "Big Four," was founded in 1989 through the merger of Ernst & Whinney and Arthur Young. It operates in more than 150 countries, offering audit, advisory, tax, and transaction services.
- Services: EY provides audit and assurance, consulting, strategy, tax, and transaction advisory services, with a focus on helping businesses improve performance and manage risk.
- Market Position: EY competes directly with PwC in the audit, advisory, and tax sectors, offering similar services to global clients. Both firms have a significant presence in financial advisory and digital consulting.
3. KPMG
- Overview: KPMG, the fourth member of the "Big Four," provides audit, tax, and advisory services globally. It operates in more than 150 countries and caters to large corporations, governments, and not-for-profits.
- Services: KPMG offers audit, consulting, tax, and advisory services, focusing on risk management, regulatory compliance, and financial services.
- Market Position: KPMG is a direct competitor to PwC in audit and assurance services, consulting, and tax advisory. Both firms serve clients in a wide range of industries, with KPMG known for its strong risk and compliance advisory offerings.
4. Accenture
Overview: Accenture is a global professional services company, specializing in digital, cloud, and security services, as well as consulting and outsourcing.
Services: Accenture offers services in digital transformation, technology consulting, IT services, cloud migration, and business process outsourcing.
Market Position: Accenture competes with PwC’s consulting services in digital transformation, technology consulting, and business process outsourcing. Accenture’s focus on innovation and technology-driven solutions makes it a strong competitor in the consulting space.
5. Grant Thornton
- Overview: Grant Thornton is a global professional services network providing audit, tax, and advisory services, particularly focusing on mid-market clients.
- Services: Grant Thornton offers audit and assurance, tax advisory, and consulting services, with a strong focus on risk management, regulatory compliance, and financial advisory.
- Market Position: Grant Thornton competes with PwC in audit and advisory services, particularly for mid-market clients. While PwC serves larger corporations, Grant Thornton’s focus on mid-market businesses allows it to compete in specific segments of the professional services market.
5. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
PwC demonstrates its commitment to social impact through comprehensive Corporate Social Responsibility programs. The company's initiatives span environmental sustainability, community development, education, and social welfare, reflecting its dedication to creating positive change beyond business operations.
Net zero by 2030 (SBTi‑validated climate plan)
PwC has committed the global network to achieve net zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2030, with science-based targets validated by the Science Based Targets initiative. The programme prioritises reducing operational emissions (scopes 1 and 2), lowering business travel emissions, transitioning to renewable electricity, engaging suppliers to adopt science-based targets, and using high-quality carbon removals for residual emissions—supporting climate resilience for communities and the environment.
New world. New skills. (Global upskilling for society)
New world. New skills. is PwC’s flagship social impact initiative focused on building digital, financial, and green skills within PwC and across communities. Delivered with schools, NGOs, and public bodies, it combines free learning resources, mentoring, and partnerships to expand access to quality education and help people succeed in a changing, technology-enabled economy.
Foundations and humanitarian response
Member firm charitable foundations—such as The PwC Charitable Foundation, Inc. (US) and the PwC Foundation (UK)—provide grants and volunteer support that advance education, social mobility, and community resilience. These foundations mobilise rapid relief funding during crises and support health, wellbeing, and recovery initiatives in affected communities.
Pro bono and skills‑based volunteering
PwC professionals deliver pro bono and low‑bono services to nonprofits and social enterprises, strengthening capabilities in strategy, finance, technology, cybersecurity, climate reporting, and governance. This skills transfer helps mission‑driven organisations scale their impact across education, inclusion, health, and climate action.
Responsible supply chain and human rights
PwC’s Global Supplier Code of Conduct and human rights commitments set expectations on labour practices, ethics, environmental stewardship, privacy, and information security. Supplier due‑diligence and modern slavery risk management are embedded in procurement, and PwC encourages key suppliers to set science‑based emissions targets—supporting fair work and more sustainable value chains.
Diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI)
PwC’s global inclusion strategy promotes equal opportunity, fair pay, and a culture of belonging. Actions include leadership accountability for DEI outcomes, transparent reporting, mentoring and sponsorship programmes, accessible workplace practices, and active employee networks—benefitting PwC people and the wider communities they serve.
6. Career Opportunities at PwC
PwC offers diverse career paths across its global operations, providing opportunities for professionals at various stages of their careers. The company's commitment to talent development and inclusive growth creates an environment where individuals can build meaningful and impactful careers.
Job Profiles and Departments
Explore the wide range of professional opportunities available across PwC's organizational structure:
- Assurance (Audit & Trust Services): Roles include external audit, internal controls, SOX/ICFR, technology-enabled audit delivery, and assurance over non-financial information (including sustainability/ESG reporting such as CSRD). Responsibilities span planning and executing audits under PCAOB/ISA standards, leveraging platforms like Aura, Halo, and Connect, and delivering high-quality, data-driven assurance. Skills: accounting and auditing standards, data analytics, risk assessment, stakeholder communication, and emerging reporting frameworks. Career progression typically moves from Associate to Senior Associate, Manager, Senior Manager, and Partner.
- Consulting (Strategy, Transformation & Technology): Advises clients on strategy, operating model, finance transformation, cloud and digital, cyber, deals integration/separation, and customer-led growth. Consultants work on problem framing, solution design, delivery, and change management, often in agile, cross-functional teams. Skills: structured problem solving, storytelling, stakeholder management, data & analytics, cloud (AWS/Azure/GCP), cyber, genAI, and product thinking. Clear pathways exist from Associate/Consultant to Senior Associate, Manager, Senior Manager/Director, and Partner.
- Tax & Legal Services: Covers corporate and international tax, transfer pricing, indirect tax/GST/VAT, global mobility, controversy, compliance, and tax technology. Increasing focus on managed services and technology-enabled compliance/reporting. Skills: tax law and accounting, regulatory interpretation, data modeling, automation, and tax platform proficiency. Careers progress from Associate to Senior Associate, Manager, Senior Manager, and Partner (with opportunities in specialist legal practices where permitted).
- Deals (M&A, Value Creation & Restructuring): Supports the deal lifecycle: strategy, commercial/financial/operational due diligence, valuation, business modeling, integrations and separations (PMI/Carve-outs), restructuring and turnaround, and capital markets readiness. Skills: corporate finance, accounting, sector knowledge, analytics, and project leadership. Progression typically follows Associate → Senior Associate → Manager → Senior Manager/Director → Partner, with options to specialize by industry or capability.
- Risk, Regulation & Forensics: Focuses on enterprise risk, internal audit, controls and compliance, financial crime, cybersecurity, privacy, resilience, and forensic investigations/disputes. Teams help clients design and operate control frameworks and respond to incidents. Skills: risk frameworks (COSO/ISO), controls testing, regulatory insight, cyber and privacy standards, investigative techniques, and data analytics. Offers specialist tracks and leadership roles across industries.
- Technology & Digital (Cloud, Data, AI & Cyber): Engineers, architects, data scientists, and cyber professionals build and operate digital solutions, including genAI-enabled platforms, data modernization, cloud migrations, and managed services. Skills: Python/SQL, ML/GenAI, data engineering, DevOps/SRE, security architecture, and cloud certifications (AWS/Azure/GCP). Career paths include technical specialist, solution architect, product manager, and leadership roles, with opportunities to gain certifications and work on global platforms.
Growth and Development Opportunities
PwC invests significantly in employee development through structured programs and initiatives:
- PvC Professional Leadership Framework: A firmwide leadership framework that guides development at every grade, emphasizing whole leadership, business acumen, technical capabilities, global acumen, and relationships. It provides clear expectations, feedback mechanisms, and coaching to help individuals grow into trusted, inclusive leaders who deliver sustained outcomes.
- New world. New skills – Upskilling at Scale: Ongoing investments to upskill all people in digital, data, and AI—through structured learning pathways, digital badges, formal training (including cloud/cyber certifications), and hands-on labs. PwC also deploys proprietary learning platforms and alliances (e.g., with major cloud providers) to ensure current, market-relevant skills.
- Global Mobility and Cross-Border Experience: Opportunities for short-term projects, virtual teaming, and longer-term secondments across PwC’s global network and Acceleration Centers. This exposure builds cross-cultural collaboration, broadens sector expertise, and strengthens consulting and leadership capabilities.
- Innovation and GenAI Programs: Access to innovation labs, accelerators, and a growing GenAI Center of Excellence that helps teams co-create client solutions using responsible AI. Employees can contribute to citizen-led automation, experiment in secure sandboxes, and scale reusable digital assets across lines of service.
- Diversity, Inclusion and Well-being: Firmwide inclusion initiatives, employee networks, and well-being programs (e.g., Be Well, Work Well) support a sustainable career. Many territories offer hybrid-working options, mental health resources, and competitive benefits; specifics vary by member firm but share a focus on inclusion and flexibility.
7. Future Outlook and Strategic Plans
This section presents PwC's official strategic direction based on investor presentations, press releases, and sustainability reports. All information is sourced from verified company communications and reflects confirmed initiatives and goals.
PwC's future strategy is structured around key focus areas designed to align with global market trends and industry evolution:
1. Technology and AI-enabled Transformation
PwC is scaling technology and AI to enhance quality, speed, and impact across audit, tax, and consulting. Under The New Equation strategy, the firm continues multi-year investments in digital platforms, data, cloud, and responsible AI to deliver trusted outcomes at scale. PwC US announced a dedicated multi-year investment to accelerate generative AI adoption with strategic alliances, while the network has expanded secure, enterprise-grade AI tools for its people. The focus includes embedding AI into core delivery, modernizing data estates, and co-creating industry solutions with leading hyperscalers. Equally important is governance—PwC emphasizes risk, security, and responsible AI principles in design and deployment to maintain trust.
- PwC US announced a $1 billion investment over three years (2023) to expand and scale its AI capabilities with Microsoft and OpenAI.
- Largest enterprise rollout of ChatGPT Enterprise: 100,000 licenses across PwC’s US and UK firms (2024), alongside becoming OpenAI’s first reseller partner.
- Expansion of alliances with Microsoft, Google Cloud, AWS, SAP, Oracle, Salesforce, and others to build domain-specific digital and AI solutions.
- Continued delivery of The New Equation’s multi-year technology investments through FY26 to enhance quality, automation, and client outcomes.
2. Sustainability and ESG Goals
Sustainability is a core pillar of PwC’s strategy, anchored by a science-based net zero commitment for 2030. The firm focuses on decarbonizing its operations, transitioning to renewable electricity, reducing business travel emissions, and engaging suppliers to set science-based targets. PwC supports clients with ESG strategy, reporting, and assurance, including readiness for evolving regulations such as the EU’s CSRD. The firm reports progress annually and integrates climate risk and opportunities into its own governance and operations, reflecting its long-term commitment to building trust and delivering sustained outcomes for stakeholders.
- Net zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2030 with validated science-based targets, including a 50% reduction in Scope 1 and 2 emissions and in business travel emissions intensity by 2030.
- 100% renewable electricity target (RE100) across operations, supported by renewable energy procurement where available.
- Supply chain engagement target for a majority of suppliers by spend to set science-based targets by 2025.
- Scaling sustainability reporting and assurance services globally, including support for CSRD readiness and assurance in the EU.
3. Market Expansion
PwC is deepening its presence in priority growth areas and client segments, expanding managed services, and strengthening regional delivery capabilities. The firm is scaling its global network of Acceleration Centers to provide technology-enabled delivery, while broadening services for private and mid-market clients via PwC Private. In Europe, demand for sustainability and reporting assurance is increasing with CSRD, and PwC is expanding related capabilities. Strategic alliances with major technology providers continue to open new routes to market as clients modernize their data, cloud, and ERP estates and seek industry-specific solutions.
- Expansion of sustainability/ESG reporting and assurance services across the EU to support CSRD implementation timelines.
- Scaling Managed Services across tax, finance, risk, cyber, and cloud to provide outcome-based, technology-enabled operations.
- Strengthening the global Acceleration Centers network (e.g., India, Poland, Mexico, China, and Manila) to support cross-border delivery at scale.
- Focused growth in the private and mid-market segment through the PwC Private platform and sector-led offerings.
4. Innovation and R&D
PwC invests in building proprietary digital products, reusable assets, and accelerators that embed data, automation, and AI into services. The firm’s assurance technologies and industry platforms continue to evolve, while genAI Centers of Excellence orchestrate rapid experimentation with responsible guardrails. PwC co-develops solutions with alliance partners and codifies leading practices into repeatable, technology-enabled delivery. Innovation also focuses on quality—strengthening audit technology, augmenting risk and compliance tooling, and industrializing data pipelines that drive faster, more trusted insights for clients.
- Ongoing investment under The New Equation to develop digital products and innovation hubs, including genAI Centers of Excellence.
- Enhancements to assurance technologies (e.g., Aura, Halo, and Connect) to increase audit quality and analytics coverage.
- Co-creation of sector solutions with hyperscalers and major SaaS providers to accelerate time-to-value.
- Continued development of reusable accelerators and assets, with IP managed under PwC’s global products and platforms governance.
5. Talent and Workforce Strategy
PwC’s people strategy centers on attracting, developing, and retaining diverse talent while equipping everyone with digital and AI skills. The firm’s leadership framework and upskilling programs support continuous learning, certifications, and career mobility. PwC’s New Equation included commitments to significant hiring and skills investment, complemented by flexible work practices (as locally applicable) and well-being programs. The firm also publishes transparency and ESG reporting that reflects progress on inclusion and workforce priorities, reinforcing its commitment to a values-led culture.
- Hiring and capability build aligned to The New Equation, including creating tens of thousands of roles in areas like technology, cyber, cloud, and ESG.
- Global DEI programs and transparent reporting through annual reviews and local transparency reports.
- Firmwide digital and AI upskilling, including structured pathways and industry-recognized certifications.
- Global mobility opportunities and hybrid working models (programs and policies vary by member firm and jurisdiction).
6. Financial Performance Goals
As a global network of partnerships, PwC focuses financial strategy on sustainable growth, quality, and reinvestment rather than shareholder distributions. Capital is allocated to technology, talent, alliances, and quality management systems that strengthen trust and drive long-term client impact. The firm publicly discloses revenue and strategic progress in its annual global review and communicates multi-year investment programs that underpin future growth.
- Multi-year $12 billion investment under The New Equation (announced 2021) to enhance technology, talent, and ESG capabilities through FY26.
- PwC US’s $1 billion investment over three years (announced 2023) to accelerate GenAI adoption and build AI-enabled solutions.
- Not applicable: PwC’s partnership model does not include dividends or share buyback programs.
- Ongoing efficiency initiatives through standardized platforms, managed services, and Acceleration Centers to improve delivery leverage and quality.
8. Latest News & Updates about PwC
Stay informed with the latest updates from PwC, including insights into global consulting, tax, and advisory services. Learn how PwC is driving business transformation through innovation, strategic partnerships, and thought leadership across industries.
9. Conclusion
PwC is a global leader in professional services, known for its client-centric approach, commitment to innovation, and expertise in areas like digital transformation, regulatory consulting, and sustainability. With a strong focus on expanding digital and technology services, driving ESG initiatives, and growing in emerging markets, PwC offers exciting career opportunities across audit, consulting, tax, and advisory. Aspiring candidates can prepare for a rewarding career at PwC by aligning their skills with the firm’s mission to help clients solve complex business problems and navigate a rapidly changing world.
Key Takeaways for Aspiring PwC Candidates:
- Research the Company: Understand PwC’s core service offerings, including its leadership in consulting, audit, and tax. Be familiar with PwC’s global presence and how it helps clients solve complex business challenges.
- Prepare for the Interview Process: For technical roles, focus on domain-specific knowledge in audit, tax, or technology. For consulting and advisory roles, be ready to discuss market strategies, regulatory changes, and risk management.
- Demonstrate Cultural Fit: PwC values leadership, collaboration, and innovation. Highlight your ability to contribute to PwC’s growth by solving real-world business challenges and improving client outcomes.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest trends in consulting, digital transformation, and regulatory changes. Understanding these trends will help you stand out during the interview process.
