- Explore [has_child]
- All Courses [subitem]
- AI Career Platform [subitem]
- Hire form us [subitem]
- 1:1 Coaching/Mentoring [subitem]
- Job Board [subitem]
- Institute Partnerships [subitem]
- Resources [has_child]
- Master Classes [subitem]
- Discussion Forum [subitem]
- Coding Playground [subitem]
- Free Courses [subitem]
- Topics [has_child]
- Data Science [subitem]
- Software Development [subitem]
- Company Insights
- Interview Preparation [subitem]
- Python [subitem]
- Programming [subitem]
- Digital Marketing [subitem]
- Web Development [subitem]
- Success Stories [subitem]
Data Structures: Foundation of Effective Programming
Fundamentals of LCM and HCF-2
A Career in Digital Marketing - A Complete Guide for Beginners
Advanced Algorithms and Problem Solving Techniques
Basic Guide to HTML & CSS – The Fundamentals of Web Development
6 Bootstrap Tools and Playground – One-stop shop for all Web Developmental Needs
Why is it Important for Freshers to Work in a Team?
The Role and Importance of Banks in the Economy
The skills required to stay relevant in IT sector
Basics of Javascript
Python Libraries
Why Learn English?
Introduction to Big Data
Introduction To Cloud Computing
What Is Content Marketing?
10 Common Data Structures Every Programmer Must Know
What is the Scope of Digital Marketing in 2025
Operating System: Functions
Discover the Versatility of Microsoft Excel: Your Swiss Army Knife for Data
React Functional Components: Introduction
What is Digital Marketing & How to Become a Digital Marketer
Introduction to Natural Language Processing (NLP)
What is Meant by Machine Learning & What Can Machine Learning Do?
Fundas of Pandas
Why Data Visualization is Important for Becoming a Data Scientist
C++ Language: An Overview
Fundamentals of Divisibility Rules in Quantitative Aptitude
Javascript vs Typescript: What is the Difference?
What is Email Marketing in Digital Marketing?
How To Start Competitive Programming - A Complete Guide
A quick guide to Asymptotic Analysis
OOPs (Object Oriented Programming) in C++
What are Node.js and Basics of Node.js?
A-Z about Python Variables
What is Consulting? Essential Insights for Aspiring Consultants
What are Collections in Python?
Header in C++
Learn about Boolean in Python
Most Common 10 Telephonic Interview Questions
Mastering Vocabulary: The Key to Verbal Ability
Ultimate Guide to HR Interview Questions for Freshers
Understand Serialization and Deserialization in Java
What is a Job Interview?
The Ultimate Guide to Resume building for Freshers
All About Resume and Its Importance
Data Science vs. Data Analytics - What's the Difference?
Secrets Of A Good Resume, Which Will Get You Hired!
How To Start Your Career In Data Science
Java Programs: Know the Best Java Programs for Beginners
JSON vs XML: Differences
Software: Types & Definition
Does a Linkedin profile really matter before getting a Job?
How to Apply for Jobs as Fresher & Get Selected in One Go
What is Full Stack Development?
Encapsulation in Java: A Comprehensive Tutorial
The Multifaceted Relationships Between Banker and Customer
Why Group Discussion for Interview? The HR Perspective
Getting Started with Tableau: Installation and Introduction
Software Testing: What it is?
What is Grooming & Etiquette?
Step-by-Step Guide to Data Visualization with Power BI
Job Trends In This Decade
What is Search Engine Optimization & How It Works
Fundamentals of Digital Marketing
Introduction To SQL: A Complete Guide
Introduction to Goal Setting and Risk Profiling
Types of Data in Statistics
Data Communication: A Process
Introduction to Management Interview Preparation
All about C Programming Language
Structure of DBMS
Introduction to Deep Learning: From Basics to Advanced Concepts
Why Social Media Marketing Is Important?
Introduction to Big Data Analytics: From Basics to Implementation
System Testing: Explained
Master Simple and Compound Interest Quickly and Accurately
Creating and Using Sets in Tableau: A Comprehensive Guide
The Essential SUM Function in Excel: A Step-by-Step Guide
Mastering SWOT Analysis for Business Success
Understanding the Loan Underwriting Process
Mastering Data Filters in Tableau: A Step-by-Step Guide
Understanding Risk and Return in Mutual Funds
Mastering the MIN Function in Excel: Find the Lowest Value Instantly
Mastering Value Chain Analysis: Uncovering Business Opportunities
Understanding the Difference in Simple and Compound Interest over 2 and 3 Years
Understanding Credit Scoring Models: A Comprehensive Insight
Understanding PESTEL Analysis for Industry Evaluation
Creating Calculated Fields in Tableau: A Step-by-Step Guide
Understanding Principle Multiplication with Compound and Simple Interest
Mastering the GE-McKinsey 9-Box Matrix: A Strategic Guide
Combining Data Sources Using Data Blending in Tableau
Mastering the COUNT Function in Excel
Understanding Simple Interest vs. Compound Interest
Mastering Mutual Fund Investment and Redemption Plans
Understanding Credit Rating Agencies and Their Processes
Mastering Mixtures and Alligations: Key Techniques and Practice
Mastering the COUNTA Function in Excel
Bringing in More Data with Joins in Tableau
Maximizing Organizational Performance with the Balanced Scorecard
The Role of Financial Planning in Wealth Creation
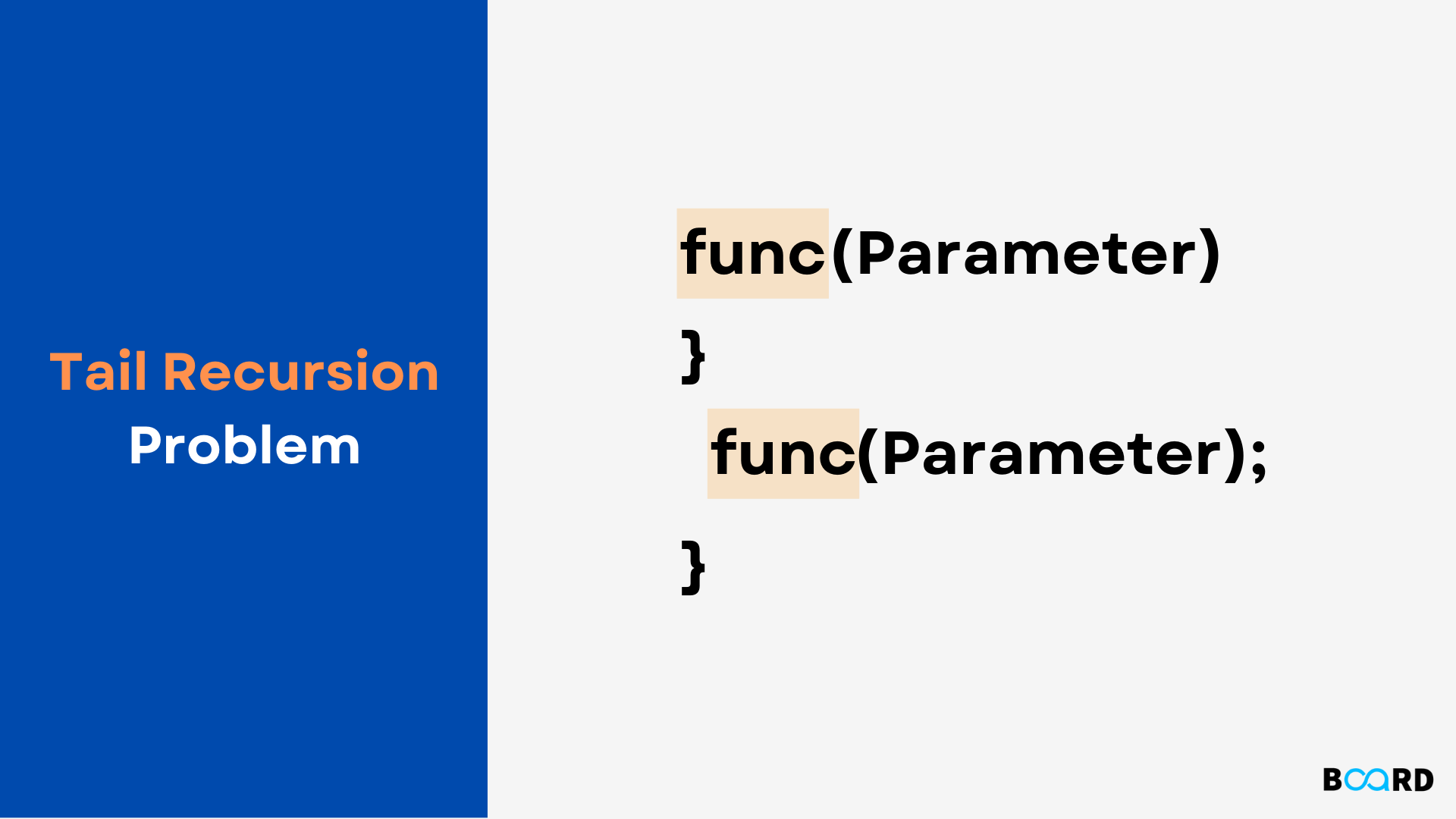
In this article, we will discuss tail recursion. The tail recursion is that kind of recursion in which the recursive call is made at the end of the function. In other words, no statement exists after the recursive call.
Let us consider the following in C++ that demonstrates how tail recursion works:
Source Code:
// Header file |
Output:
Please note that in the above program there is no statement to be executed after the recursive call.
Need for the tail recursion
The tail recursion is always preferred over the non-tail recursion as the compiler can easily optimized tail recursion.
The compiler is generally responsible for executing recursive statements with the help of a stack. The stack keeps all the necessary information including the value of parameters for each and every recursive call. Whenever there is a call made to a procedure, the information is passed to the stack, and the moment when the execution of the function ends, the information is popped out or removed from the stack. So, the problem that persists with the non-tail recursion functions is that non-tail recursive functions take more stack depth as compared to tail recursion.
How the compiler optimizes tail recursion?
The tactic utilized by the compiler to optimize the tail recursion is simple. Actually, there is no statement to be executed after the tail recursive statement so the compiler doesn’t have to worry about saving the current function’s stack frame.
How to convert a non-tail recursion into tail recursion?
We can convert most of the non-tail recursive functions into tail recursion. For example, consider the following program that computes the sum of the first N natural numbers. The below program looks like a tail recursion but it is not actually. This is because first, we calculate the result of the operation myFunction(number + 1) and then apply the addition with the number and then return the entire value. So calling the recursive function is not the last thing being done here.
Source Code
// Header file |
Output:
We can easily convert the above non-tail recursion into tail recursion. The idea is to pass an additional argument to myFunction and return the recursive call as a whole at the end of the function. For example, consider the following that computes the sum of N natural numbers using tail recursion:
Source Code:
// Header file |
Output:
Conclusion
In this article, we discussed an important data structures concept, tail recursion. We believe that you must have learned something new through this article.
