- Explore [has_child]
- All Courses [subitem]
- AI Career Platform [subitem]
- Hire form us [subitem]
- 1:1 Coaching/Mentoring [subitem]
- Job Board [subitem]
- Institute Partnerships [subitem]
- Resources [has_child]
- Master Classes [subitem]
- Discussion Forum [subitem]
- Coding Playground [subitem]
- Free Courses [subitem]
- Topics [has_child]
- Data Science [subitem]
- Software Development [subitem]
- Python [subitem]
- Programming [subitem]
- Digital Marketing [subitem]
- Web Development [subitem]
- Career Development [subitem]
- Success Stories
Data Structures: Foundation of Effective Programming
Advanced Algorithms and Problem Solving Techniques
What is Full Stack Development?
All About Resume and Its Importance
Secrets Of A Good Resume, Which Will Get You Hired!
What is a Job Interview?
What is Meant by Machine Learning & What Can Machine Learning Do?
What is the Scope of Digital Marketing in 2023
What is Digital Marketing & How to Become a Digital Marketer
What is Search Engine Optimization & How It Works
What Is Content Marketing?
Basics of Javascript
The skills required to stay relevant in IT sector
Basic Guide to HTML & CSS – The Fundamentals of Web Development
6 Bootstrap Tools and Playground – One-stop shop for all Web Developmental Needs
Does a Linkedin profile really matter before getting a Job?
What are Node.js and Basics of Node.js?
What is Email Marketing in Digital Marketing?
Most Common 10 Telephonic Interview Questions
The Ultimate Guide to Resume building for Freshers
Why is it Important for Freshers to Work in a Team?
Introduction to Natural Language Processing (NLP)
How to Apply for Jobs as Fresher & Get Selected in One Go
Introduction to Big Data
Why Data Visualization is Important for Becoming a Data Scientist
Why Learn English?
Fundas of Pandas
Why Social Media Marketing Is Important?
Introduction To Cloud Computing
Job Trends In This Decade
Types of Data in Statistics
10 Common Data Structures Every Programmer Must Know
How To Start Your Career In Data Science
Ultimate Guide to HR Interview Questions for Freshers
Java Programs: Know the Best Java Programs for Beginners
How To Start Competitive Programming - A Complete Guide
Understand Serialization and Deserialization in Java
A quick guide to Asymptotic Analysis
A-Z about Python Variables
What are Collections in Python?
Learn about Boolean in Python
Data Science vs. Data Analytics - What's the Difference?
OOPs (Object Oriented Programming) in C++
Javascript vs Typescript: What is the Difference?
Software: Types & Definition
Software Testing: What it is?
Introduction To SQL: A Complete Guide
React Functional Components: Introduction
JSON vs XML: Differences
All about C Programming Language
Structure of DBMS
C++ Language: An Overview
Header in C++
Encapsulation in Java: A Comprehensive Tutorial
Data Communication: A Process
Python Libraries
Operating System: Functions
Fundamentals of Digital Marketing
What is Grooming & Etiquette?
Why Group Discussion for Interview? The HR Perspective
Introduction to Big Data Analytics: From Basics to Implementation
Introduction to Deep Learning: From Basics to Advanced Concepts
Introduction to Goal Setting and Risk Profiling
System Testing: Explained
The Ultimate Basic Resume Format & Structure Guide
5 Common Resume Mistakes That You Need to Avoid
Prerequisites For A Job Interview
How To Ace a Walk-In-Interview
What is Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning?
Difference between Data Analyst, Data Scientist & Business Analyst
Most important Python Libraries for Data Science
Basic Guide to Become Full Stack Developer from Scratch
Social Media as a Job Platform
Most Important Fundamentals of Digital Marketing
Highest paying jobs of 2023 for freshers
7 Sales & Marketing Interview Questions and Answers
4 Amazing Networking Conversation Starters
10 tips for introverts on how to start networking
The trendiest topic in ML - Natural Language Processing
Resume Format for Beginners + Resume Templates Free Download
The Difference between On-Page and Off-page SEO
How to make the most out of online training programs
Career Path in Data Science: Explained
How to Search for Jobs | 7 Killer Job Search Tips for 2022
Best Data Visualization Projects for Beginners
5 Most-Common Machine Learning Mistakes to Avoid as a Beginner
How to Hone Your English Communication Skills?
Digital Marketing Trends in India
Why Should You Use Bootstrap?
Functional Components and Class Components in ReactJS
The Rise of Big Data
What is Content Marketing and Types of Content Marketing?
Interesting Java Project Ideas For Beginners
An Ultimate Guide To Email Marketing
Python data Types
Searching Algorithm and its Types
Learn to Create DataFrames using Pandas
A quick guide to Stack Class in Java
Understanding Array Slice() in JavaScript
Most Important Linux Commands
A Quick Guide to NPM
Quick Guide to Abstract Data Types
Difference Between C and C++ Programming Languages
How To Add Horizontal Line In Html
Introduction to STLC (Software Testing Life Cycle)
A Quick Guide to Breadth-First Search
Java Vs Javascript: What's The Difference?
SQL Commands-An Introduction
Cloud Based Services
Python Function
Applications of DBMS
LAN and WAN: Differences
Hardware vs Software
Counter in Python
Displaying A to Z characters using a loop: C++ Program
ord() in Python
C++ Pointers
Decision Making in C
String Array in Java
Understanding and Influencing Consumer Behaviour
Is Grooming Really Worth The Effort?
Types of Group Discussion Topics
Introduction to the Hadoop Ecosystem: An In-depth Exploration
Deep-Dive into Neural Networks
A Comprehensive Guide to Investing and Insurance in 2023
Modules in Python
Class Methods in Python
Selection Sort In Python
Glob() in Python
Turtle in Python
Python Pyramid Pattern Program
XML Parsing in Python
The Basic Skills That You Should Not Put on a Resume
Tips for Resume Writing & Resume Mistakes That You Should Avoid
How To Prepare For An Interview
Concept of Big Data and Types of Big Data
A-List of the Top Machine Learning Algorithms in Python
5 Major Skills Required for Success in Digital Marketing
How To Write The Best Career Objective Statement for a Resume
Top 4 Data Science Job Interview Questions And Answers for Freshers
Types of Job Roles Available in the Field of Data Science
How to Ace in the Field of Analytics?
Ultimate 6 Steps to Search Job in India
Creating APIs using Express in Node.js
Best Career Options After Graduation
Difference between Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning
Why Are Online Training Programs Better Than Offline Training?
How to start professional networking in college
8 Digital Marketing Trends for 2023
Why Self-Motivation is important for a Fresher
4 Social Media Trends During the Lockdown
Top 10 Content Writing Tips for Beginners
What is Tableau?
10 Quick Video Call Interview Tips For Everyone
Five Technical SEO Practices NOT To Avoid
Is Email Marketing Dead?
How to Become a Front-End Developer – Complete Roadmap(2023)
OOPs Concepts In Java
Depth First Search (DFS) with Explanation and Code
A Simple Introduction to Recursion
What is Hashing in Data Structure?
Understanding Loops in C++
A Quick Guide to String Builder in Java
Working of Jump Statements in C++
How to Build a Chatbot in 10 Minutes?
Understanding setState in Reactjs
A Quick Guide to Encapsulation in C++
Introduction to Fork Call
Converting List to DataFrames in Pandas
How to Become a Data Scientist – A Complete Road Map of 2023
Arrays In Python
JavaScript: Array Filter() Method
JavaScript console.log() Method
Software Quality Assurance in Software Engineering
Databases Types
What is Application Software?
Learn about Cloud Computing Architecture
String Concatenation in Python
Lambda function in Python
GET and POST requests
Operator Precedence and Associativity in C
HashMap in Python
SASS and SCSS: Explanation and Differences
Network Topology
Linking A Button To A Page in HTML: Here’s How?
Reverse an Array in Java
Char and Varchar in SQL
Strategies and Techniques in Social Media Marketing
Grooming Guidelines For Women
Techniques & Tips for Group Discussion: Verbal
Introduction to Apache Pig: A High-Level ETL Tool in the Hadoop Ecosystem
Build Your First Neural Network: A Step-by-Step Guide
Introduction to Equity Investing
String formatting in Python
How to Write a Good Resume
5 Resume Writing Myths That You Need to Stop Following Now!
International Women's Day | In Conversation with Vishakha Vartak
How To Introduce Yourself During An Interview
Why Are Companies Hiring Big Data Analysts?
Top 6 Web Developer Job Interview Questions And Answers
Artificial Intelligence vs Machine Learning vs Deep Learning vs Data Science
Top Web Development Trends in 2022
Express as the most popular Node.js framework
5 Things You Should Be Doing on LinkedIn (Even if You're Not Job Searching)
Anatomy of a Digital Marketer
How To Reduce Procrastination And Be More Productive
How to Write a Job Application email to the HR of your Dream Company (with sample)
Is Email Marketing Dead, or Are You Doing It Wrong?
What are Hackathons? Their Importance in Data Science?
4 Things You Can Do During Lockdown (Not an Online Course)
Ways To Ace Video Interview
What will Digital Marketing in India look like in 5 Years?
Top 20 Sample Career Objectives For Your Resume
Top 5 Machine Learning Algorithms every Data Scientist should Know
The Right Way to Lure the Audience with Content
Proven ways to be a Data Scientist Without a Degree
Why Should You Learn Tableau?
Why Social Media Presence Is Important For Business
What is the Purpose of Search Engine Marketing?
10 Best Career Options After B.Com
The Most Popular Front-End Frameworks To Use In 2023
Difference Between BFS and DFS (with code and diagrams)
Abstraction Vs Encapsulation in Java
Command Line Arguments in C++
Understanding Garbage Collection in Java
How to Build a TreeMap?
Learn everything about useState in React
Learn about Attributes in DBMS
A Quick Guide to STAR Topology
How to Get Column Names in Pandas?
How to use the bgcolor attribute in HTML?
A Quick Guide to Waterfall Model in Software Engineering
Linear Regression in Python
Inline Functions in C++
5 Cloud Deployment Models: Detailed Explanation
Learn about System Software
Arrays vs Linked List
Python print() Function
How to run a .js file in Terminal?
Ternary Operator in Python
One Dimensional Array in C
JavaScript array map() method
ORDER BY in SQL
XML and JSON: Explanation and Differences
Process Vs Thread: Explanation and Differences
List vs Tuple: Differences
OOPs Abstraction in C++
Converting Character Array to String in Java
Navigating Social Media Ads - Establishing and Managing Ad Accounts
Grooming Guidelines For Men
Deep Dive into Apache Hive Database
Deep Dive into Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)
A Deep Dive into Mutual Funds
This is why you should be a career coach!
4 Elements of a Power Resume
Do's and Don'ts of Resume Writing | Key Resume Writing Guidelines
Women's day special: In Conversation with Dr. Shoma Shrivatava
How To Make a Great First Impression In an Interview?
Day in the Life: Roles & Responsibilities of a Data Scientist
How Companies Use Big Data Effectively To Make Data-Driven Decisions
Top 6 In-demand Digital Marketing Skills That You Must Have
How To Write a Cover Letter for Career Change - With Free Sample
How Students Can Focus on LinkedIn for Remarkable Career Growth?
Best Tools for Data Visualization in Data Science
A Beginner’s Guide to YouTube Marketing
Technical Interview Q&A for Fresher Data Scientists
How Can Working Professionals Make The Most Out Of Online Learning
The Most Important Types of Machine Learning Models
5 Best Career Options After Engineering
5 Grooming and Etiquette Guidelines for a Zoom Interview
10 Best Sample Career Objective in Resume Templates
Fundamentals of Express.js
Benefits of Using AngularJS
Data Science Vs Machine Learning
Why Digital Marketing Is Vital For Any Business?
Data Science Projects for Beginners to do During this Lockdown
YouTube SEO Tips: Fastest Way to Rank #1
How to Start a Career in Digital Marketing
Best Resources for Back End Development
Understanding Overloading in Java
How to Plot in Python using Pyplot?
Implementing 2D Arrays in C
What are Functional Interfaces in Java?
How to Perform Level Order Traversal?
Learn about Strings in C++
CSS Float Center Element - Everything You Need To Know
What Is The React Component Lifecycle?
How does CPU Scheduling work?
Difference between Hashmap and HashTable
A Quick Guide to Entities in DBMS
Learn about Reset Index Pandas
Local vs Global Variable in Python
Everything you need to know about Strings in Python
Understanding Substr() Function in C++
How to Read a File in Node.js?
Cloud Computing Virtualizations | Types of Cloud Computing Virtualizations
Stack in Data Structure
GROUP BY in SQL
System Software vs Application Software: Differences
How To Create Engaging Content For Your Email Marketing Campaign?
Encoding and Decoding URL in JavaScript: How?
List vs Set: Key Differences
OOPS Polymorphism with C++
String to Array conversion in JavaScript
Pojo Class in Java: How to Create?
Mesh Topology in Computer Networks: Pros and Cons
Best Plagiarism Checkers Instead of Turnitin in 2023
Mastering the Art of Paid Advertising
Mastering Business Etiquette
Group Discussion Techniques: Non Verbal
All About Sqoop: The Data Ingestion Tool in the Hadoop Ecosystem
Advanced CNN Architectures and Training Techniques
Learn Tax Planning in 2023
Best Fonts & Font Sizes to Use in a Resume
How Many Pages Should An Ideal Resume Be?
International Women's Day | In conversation with Sahana HS, Board Infinity Coach
10 Common questions asked in an Interview
What Is The STAR Interview Method?
How Career Coaching Sessions Can Help You To Easily Get Your Dream Job?
How To Write Your Career Summary in Resume (with Sample)
Introduction to Machine Learning with Python
3 Key areas for Application of Big Data in Decision Making
Best Beginner Data Science Projects That You Can Start Today!
How to write a job offer acceptance email with a sample
How to become an SEO Expert?
7 Tips to Find Data Science Internships
How To Leverage Social Media Marketing for Business Growth in 2022
Complete Guide To Decision Tree Algorithms for Beginners /w Examples
Are Paid Online Certification Courses Worth It?
6 Tips on How to Get More Followers on LinkedIn
What To Do After Engineering? [Answered]
Controlled and Uncontrolled Components in ReactJS
Single-Page Applications vs. Multi-Page Applications
5 Reasons You Need To Learn Digital Marketing In 2022
How to Avoid Spam Filter And Improve Email Deliverability
Top Cloud Service Providers In 2022: AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform
Digital Marketing Vs Traditional Marketing
Top 10 Skills to Become a Full-Stack Developer in 2022
Accenture Technical Interview Questions: Freshers and Experienced(2023)
Complete Walkthrough of Stacks in Data Structure
Understanding Singleton Class in Java
In-Depth Analysis of Struct in C
How to Handle Exceptions in Java?
What are Keys in DBMS?
A Quick Guide to Bubble Sort Algorithm
Constructor vs Destructor in C++
Learn How to Perform Union in SQL?
A Quick Guide to Backtracking Algorithm
Box Plot in Python using Matplotlib
Try-Except Block in Python (Using with Examples)
JavaScript Fetch API Explanation
How does AI Enhance your Content Writing using Paraphrase Tools?
How to add a space between the flex container and its elements?
Matplotlib Pyplot Legend
Web Development Frameworks
JavaScript Split()
iloc() function: Learn to extract rows and columns
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs)
Initializing Vectors in C++
writeFile() in Nodejs
Black Box vs White Box: Software Testing
Multiple Inheritance in C++
Website and Web Application: Differences
ListSize() in Java
File Allocation Methods
Not Equal Operator in Python
Python List append() Method
Navigating Group Discussions: The Don'ts for Success
An Introduction to Apache Spark
Estate Planning: Should You Treat Children Equally In Your Will?
Role of Social Media in Supply Chain Management
Resume Keywords: Optimize Your Resume and Get Interview Call
5 Resume Design Principles to Create the Best Resume Design
How To Answer The Question About Weaknesses In An Interview?
Tips To Become A Full-Stack Developer
5 Soft skills that every Techie should have in 2022
The Power of a Career Coach and How it can Change Learner's Career!
Why Specifically Use Python for Machine Learning?
How to Rank higher on LinkedIn search for your Skills
How to Ace an Interview that's not going too well
#SeptemberSpotlight: In conversation with coach Kunal Naik
15 Perfect Examples of Summary of Qualifications in a Resume
Demystifying Kaggle for Data Science Beginners
How To Find A Data Science Internship In 2022
Is Digital Marketing A Good Career Option?
Lucrative Career Opportunities after BBA In 2023
Benefits of Using Vue.js
Why Should You Sell Product With Digital Marketing Strategies
Elucidating Amazon Virtual Private Cloud
How to Become an SEO Analyst?
How to Get an Email Marketing Job at an MNC?
How to Write a Resignation Letter(With Samples)
Top 20 Infosys Technical Interview Questions and Answers(2023)
Solving N Queens Problem using Backtracking
Git Commands Every Developer Should Know
Top 10 Best Practices For Securing Your Node.js Application
Understanding Vectors in C++
Working on Queue using STL
A quick guide to Debounce in JavaScript
Understanding Multiple Inheritance in Java
Understanding Copy Constructor in C++
A practical guide on Synchronization in Java
useCallback: Hooks in Reactjs
A Quick Guide to White Box Testing
How to sort string in Python?
How to find the kth smallest/largest element in an array?
Joins and Its Types in SQL
How to reverse a string in Javascript?
A Quick Guide to Star Schema in Data Warehousing
Matplotlib Scatter in Python
Nested Structures in C
Try, Except, Else and Finally in Python
Primary Key and Unique Key in DBMS: Differences
Dictionary of Lists
Cellspacing and Cellpadding: What's the Difference?
Read xlsx File using Pandas
Try, Catch and Finally in Java
HTTP and HTTPS: Differences
Direct Memory Access Technique: Explanation
Virtual Base Class in C++
NPM and NPX: Explanation and Differences
Logistic Regression: Detailed Introduction
The Ultimate Do's to Stand Out and Clear a Group Discussion Round
Deep Dive into Apache Spark: Unlocking the Power of Big Data
Understanding the Impact of Loans on Your Credit Score: Strategies for Smart Borrowing
Why Are Keywords Important in a Resume?
Phone Interview Tips That Will Help You Get Hired
How To Explain Employment Gaps In Job Interview
How to Survive the Technology Revolution in 2022?
The Demand of Full Stack Developers in India
How to Make Your Skills Look Exciting on Your Resume
4 Important elements of writing a winning LinkedIn summary and headline
Machine Learning in Python: Supervised vs Unsupervised Learning
How to make a Data Science Portfolio? (To get Hired)
Booming career paths for management graduates
#SeptemberSpotlight: In conversation with coach Vinod Menon
How to write a Post-Internship ‘thank you’ letter
Every Millenial Should Make These 4 Changes To Improve Their Resume
A Career in Digital Marketing - A Complete Guide for Beginners
Ultimate Guide Explaining the 7 P’s of Marketing
How To Find The Best Data Science Career Coach?
How To Find Coaches in Data Science
Top 5 Social Media Automation Tools in 2022
React Hooks and its Advantages
How to Get a Job at Microsoft as an SEO Executive
Top 10 Node JS Project Topics You Should Try Right Away
Top 50 TCS Interview Questions and Answers(2023)
Becoming Friends with Friend Function in C++
Quick Guide to Divide and Conquer Algorithm
Learn about Generics in Java
Understanding 2D Vectors in C++
How To Embed PDF Files Using HTML - A Comprehensive Guide
A Guide to Association, Aggregation, and Composition in Java
Introduction to Hamming Code
How to Perform Insertion Sort in C++?
Implementing Queue using Stacks
How to use Merge Sort with Linked Lists
A Quick Guide to Addressing Modes in Computer Architecture
Python For Loop
Naive Bayes Classifiers - Overview
ETL Process in Data Warehouse- Description and Examples
Frontend and Backend in Web Development
Graph Plotting in Python
Promise in JavaScript
NumPy Broadcasting
Raise Keyword in Python
Cardinality in DBMS with Examples
Socket in Computer Network
Alpha and Beta testing
Type Conversion in C
Constructor Chaining in Java
Array Join() in JavaScript
Rename column name in SQL
Sort Dictionary in Python
Techniques To Initiate A Group Discussion
Mastering the Art of Investment Banking: Essential Strategies for Beginners
4 Tips for Using Keywords in a Resume
4 Places for Professional Feedback On Your Resume
How To Prepare for a Group Interviews
Tips on How to Follow Up After the Interview
CSS Frameworks - Bootstrap – Integrated HTML/CSS with JS Integration
There is a Difference between your Resume and your LinkedIn profile
6 Interesting Machine Learning Project Ideas For Beginners
Why LinkedIn endorsements and recommendations are important and How to write one?
#Septemberspotlight: In Conversation with Coach Ranjan Sinha
6 IT Interview Questions and Answers Asked in a Tech Interview
Skills Required to Become a Successful Marketing Manager
Best Data Science Case Studies of 2022
Future of Data Science in India [In-depth Guide]
Working with React Router
NodeJS vs. Spring Boot: Which one to Choose?
How to Become a Social Media Influencer at Instagram?
What A Recruiter Is Looking For While Hiring a Full Stack Developer
Top 20 SEO Interview Questions & Answers
Introduction to Caesar Cipher Algorithm
Linear Discriminant Analysis in Machine Learning
What is Promise.all in JavaScript?
A quick guide to Access Modifiers in Java
Malloc vs Calloc - Quick Note
A Quick Guide to VAR, LET and CONST
A Detailed walkthrough of the Doubly Linked List
How to perform Matrix Chain Multiplication
Understanding Boundary Value Analysis in Software Testing
How File Handling Works in C++
How to Read files in Java?
Finding Array Triplets with Given Sum
Top 10 MBA Specializations for 2023
Learn How To Compare Two Or More Datetime Entities In SQL With Examples
Python While Loop
Longest Increasing Subsequence Problem
Flask vs Django: Differences
Classful IP Addressing: What it is?
Counting Sort Algorithm: Using C++
Vector erase() in C++
Static and Dynamic Website: Differences
Process Control Block in Operating System
Domain Constraints in DBMS
Equals and == in Java: Differences
String Comparision in Python
How to Crack a Group Discussion Evaluation
Preparing for Final Placements Effectively
Types of Power Words for Resume Writing
How to Check if Your Resume is Good for Submission?
How To Ask For Interview Feedback
A deep dive into Unemployment in India and how it can be solved
MERN V/S MEAN Stack -Difference Between
Deep Learning - Dive into the World of Machine Learning!
Types of Job Roles Available in Digital Marketing
#Septemberspotlight: In Conversation with Coach Vishakha Vartak
Tools every Digital Marketer needs to learn before it is 2022
How to Create the Ideal Resume that Gets Picked by Hiring Managers?
Types of Interview Processes for Tech Positions and How to Crack them
Everything You Need to Know About Tuples in Python | Data Science
5 Tools Every Data Scientist Should Know About
How to Get a Job in Accenture as a Full-Stack Developer?
How To Create A Social Media Marketing Strategy?
Angular Vs. AngularJS: The Difference Between Angular & AngularJS
Top 10 Career Opportunities in Data Science
Understanding Templates in C++
How to Reverse a Linked List?
Understanding Polymorphism in Java
A Detailed Overview of Macros in C++
A Quick Guide to React Router DOM
How to do Form Validation
A Quick Guide to Linked Hashmap in Java
Quick Note - Greedy Programming v/s Dynamic Programming
What Is An Algorithm (Understanding The Ingredients)
Difference Between SQL and NoSQL
Var, Let and Const: Description and Differences
Integrity Constraints in DBMS
Javascript Async and Await Function
Tail Recursion Problem
Cryptography: Explanation and Types
Virtual Memory in Operating System
Dynamic Memory Allocation in C
Zip Function in Python
Ford Fulkerson Algorithm (Maximal flow problem)
Array iteration in JavaScript
Underfitting and Overfitting in Machine Learning
Drawing A 2-D Heatmap In Python Using Matplotlib
Bucket Sort Algorithm with C++
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
Abstract Class in Java
How to Behave in a Group Discussion
Why you Need to Appear for a Mock Interview Before an Actual One?
50 Power Words For Your Resume
The Myths of Full Stack Development
Integrating Node APIs with Angular
There's Something More Important Than Your Resume To Get Hired
#Septemberspotlight In Conversation with Coach Vaibhav Jain
How to Negotiate Salary with HR in an Interview
Popular Job Roles of a Freelance Digital Marketer
8 Data Science Tools Every Data Scientist Must Know
Understanding Axios in ReactJS
How to Create a Great Full Stack Developer Resume?
6 TOOLS TO SPY ON YOUR COMPETITORS
Data Science Jobs In India
Most Important HTML Interview Questions & Answers
10 Best Social Media Marketing Tools That Will Keep You One Step Ahead In 2022
Best Resources for Front-End Development
Symmetric vs Asymmetric Encryption
Things to do with OpenCV
A quick guide to Unordered Map in C++
A quick guide to async/await in Javascript
How to Disable a button in jQuery Dialog?
Understanding the LifeCycle of an Applet in Java
Understanding Anonymous Function in Javascript
Learn Different Methods to convert a List into a Tuple in Python
Understanding JDBC in JAVA
A Quick Guide to Page Replacement Algorithm
Implementing Binary Search in C++
A Quick Guide to Relational Model in DBMS
Constraints in SQL
Stack vs Heap Memory: Key Differences
Coin Change Problem: DP and Recursion Approach
Decision Tree Algorithm: Explantation and Implementation
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
Algorithm and Flowchart: Differences Explained
List in C++
Iterators in Python
Binary Tree Code Implementation
Storage Classes in C
AddEventListener() in Javascript
Runnable Interface in Java
Learn about Aggregate Functions in SQL
Top 6 Words To Avoid Writing In Your Resume
How To Correctly Follow Up after Rejection in a Job Interview
The State of Angular in 2022 – Relevance vs. Legacy status
#SeptemberSpotlight In conversation with Coach Vishal Dhikale
Step-by-Step Guide To Facebook Ads
Pathway to be a Digital Marketer
A Guide on How to Use Google Analytics for Beginners
How To Build a Career in Machine Learning
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence Tools To Learn
10 Best JavaScript Frameworks to Use in 2023
Most Important CSS Interview Questions and Answers
Data Scientist Resume - Sample & Step By Step Guide for 2023
A Definitive Guide to Knapsack Problem
Complete Walkthrough of AVL Trees
What is Composition in Java?
Data Analyst Salary in India For Freshers & Experienced
Working of Axios in React
How to Quickly Check If an Array is empty or not in Javascript?
RSA Algorithm: Concepts and Implementation
A Set Data Structure (STL) In C++
MERN Stack: What is It?
Big O Notation: Space and Time Complexity
ER (Entity Relationship Model) in DBMS
Graphs in Data Structure and Algorithm
SQL Subqueries
Print all Permutations of given String: using C++
Ajax jQuery
JavaScript Object.assign()
Dangling Pointer in C
Cross Validation In Machine Learning
Recursion in Python
Semaphore in the Operating System
Java Custom Exception
List Slicing in Python
Data Link Layer: Explanation
Trends and Tools of JavaScript in 2022
How Machine Learning is being used in Digital Marketing
Integrating Node APIs with React
#Septemberspotlight In conversation with coach Aiman Faraz
5 Basic Elements In a Resume For a Digital Marketer
Career Path in Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence: Explained
How to Crack Full Stack Developer Interviews at Startups
Recruiter’s Viewpoint While Hiring a Data Scientist
Jobs in MERN Vs MEAN Stack
Prepare for ReactJS Interview Questions
6 Ways to Increase Organic Reach on Facebook
How to Solve Subset Sum Problem?
Introduction to Deadlock in Operating System
Nested Queries in SQL - Query In Query
Understanding Servlets in Java
Angular vs React vs Vue: Which Framework to Choose in 2023
Understanding PUT and PATCH
What is Static Class in JAVA?
A Quick Guide to Circular Linked List in C++
Converting String to Float in Python
Sliding Window Problem – C++ Implementation
SHA-1 Hash Algorithm
Time Complexity: Explanation
Heap Data Structure
Object.keys() in JavaScript
DDL and DML Commands: Explanation and Differences
Dimensionality Reduction in Machine Learning
with statement in Python
Routing Table in Computer Networks
Hashcode() in Java
Function Pointers in C
Role of Big Data in Digital Marketing
The state of React in 2022 – Re-Inventing The Experience of User Interface Design
The Perfect Format for a Digital Marketing Resume
Top 5 Types of Clustering Algorithms Every Data Scientist Should Know!
In conversations with coach Vipin Hatmode | Board Infinity
Create your First ML Application using Streamlit
What Are YouTube Tags and Why Are They Important?
OOPs Interview Questions and Answers(2023)
JavaScript Interview Questions and Answers (2023)
Understanding Huffman Coding in detail
Implement Tower of Hanoi using C++
A Quick Guide to Data Flow Diagrams
How To Master Front-End Development
Understanding Java Comparator Interface
Understanding Banker's Algorithm in Operating System
Understanding the difference between JDK, JRE, and JVM
How to Read a File in JAVA?
List Index Out of Range Error in Python
Dynamic Method Dispatch in Run-Time Polymorphism
Stack using Linked List in C++
SQL WITH Clause – Tutorial and Examples
Trie Data Structure: Explanation and Examples
Relational Algebra in DBMS
Binary Search Tree: Explanation
Firewall Networking
Array find() method in JavaScript
Python Docstring
In Conversation with coach Sivaiah Kota
How To Get Your First Digital Marketing Internship In 2022
Lead Generation Process & Platforms Every Digital Marketer Should Know
How to Impress a Recruiter with ML Projects
ReactJS vs. VueJS: Understanding the Differences
What is the Best Facebook Marketing Strategy for Business?
SQL Interview Questions
Flutter vs React Native: Which is Better for Apps in 2022
Understand the working of KMP Algorithm
How to Drop a Table in PostgreSQL?
Learn about Map Stream in Java
How to Sort a Vector in C++
Checked vs Unchecked Exceptions in Java
Python Sort() Function
Rabin Karp Algorithm: C++ Implementation
Data Flow Diagram: Introduction
Network Security Explained
JSON file in Python: Read and Write
Heap Sort Algorithm
Functional Dependency in DBMS with examples
AWT and SWING in Java
Genetic Algorithm in Machine Learning
In conversation with Talent Manager at Bridge I2I on essential skills in Analytics
Importance of a Career Coach in Digital Marketing
Types of Campaign Goals on Facebook Ads: Explained
React vs. React Native: Understanding the Differences
How A Marketing Funnel Works
Java Interview Questions and Answers (2023)
Top 10 Front-End Web Development Projects For Beginners[2023]
What are Priority Queues in C++?
Understanding Activation Function in Neural Network
How to Perform Pivot in SQL?
Unified Modeling Language and Its Functioning
Difference between JSP and Servlet
Understanding Wrapper Class in Java
Priority Queue In Java
Normalization in DBMS with Examples
Longest Common Substring Problem
Job Sequencing Problem with C++
Time Complexity of Sorting Algorithms
Python 2D Array
Dictionary to JSON: Conversion in Python
In conversation with the Talent Specialist of Diageo
Soft Skills a Fresher Must Have! (Data Science & Digital Marketing)
ReactJS Project Ideas for Beginners
What is Affiliate Marketing & How to Start?
Top 50 Data Analyst Interview Questions and Answers (2023)
7 Marketing Strategies That Help To Grow Your Startup Business
Learn About Sequence Diagrams in Software Engineering
How to Remove Key from Python Dictionary?
Learn about JVM in Java
Beginner's Guide to NumPy in Python
Guide To 5 Data Structures In C++
SQL Window Function
Java Server Page: Introduction
Longest Common Subsequence problem: solved
Second Normal Form in DBMS
Biconnected Graph Algorithm with C++
Load Factor and Rehashing
Servlet Life Cycle
Clustered and Non-Clustered Index
In Conversation with the CEO of the fastest growing Analytics Company
How to find the Best Digital Marketing course in India
7 Important Tips to Run Perfect Lead Generation Campaigns on Facebook
Introduction to Affiliate Marketing explained with Case Study
How to Prepare for FAANG Interviews?
Left Shift Operator in C++
What are Sets in Javascript?
Understand HashSet in Java
A Quick Guide to Manacher's Algorithm
Find Nth Highest Salary in SQL
Volatile Keyword in Java
Numpy in Python
Java Design Pattern: Factory Method
File Organization in DBMS
Python dictionary values()
Hamiltonian Path Algorithm with C++
DBMS vs RDMS: Key Differences
Finite Automata Explained
Founder of Dextro Analytics shares what the World of Analytics want
5 FREE Digital Marketing Certifications that You Must Have
LinkedIn as a Marketing Platform - Paid Ads, B2B vs B2C & More
How to Crack a Data Science Interview
Why Is Paid Advertising Important For Business?
Learning About Bipartite Graphs
Working of Correlated SubQueries in SQL
Learn how to do Pyramid Pattern printing in Java
Converting String to Dictionary in Python
Bitwise Operators In C++
Indexing in DBMS
Java Array and ArrayList: Differences
Map in JavaScript
Collectors toMap() in Java
Pushdown Automata: Explained
Introduction to ES6
This Analytics Professional Shares Her Expectation from the Aspirants
How To Become a Social Media Manager in 2022
4 Data-driven Marketing Roles You Should Consider If You Love Numbers
Learning Digital Marketing - A Sprint or a Marathon?
How To Ace Data Science Interviews
How to perform Matrix Multiplication with Numpy Python
Learn about Thread Sleep Method in Java
Learn about Stored Procedures in SQL
rand() Function in C++
Booth’s Algorithm
Graph Coloring Problem: Explained
Socket Programming in Java: Comprehensive Guide
Regex in Java
INDEX in SQL
Bytes to String in Python
Lead - Data Scientist of Quantzig shares thoughts about the World of Data Science
Digital Marketing Interview Questions & Answers for everyone
Top 10 Features of ES6
How to Crack an Accenture Interview for a Social Media Moderator?
Digital Marketing Salary in India 2022 - Average to Highest
Top 50 Data Science Interview Questions And Answers
Learn about Throw and Throws in Java
Triggers in SQL: An Overview and Example
What is pandas in python - Pandas Introduction
Static variables in C++
SELF JOIN IN SQL
Detect Cycle in Direct Graph
SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS
Python reduce() function
Packages in Java
Kadane's Algorithm with Java
Change has to come from both sides- the Employer and the Employee
Top Digital Marketing Interview Questions and Answers (HR Round)
20 Digital Marketing Projects for Beginners
How to Crack Data Science Interviews in the Big 4s
How to get a job at IBM as a Social Media Manager?
Verification V/S Validation in Software Engineering
Introduction to StringBuffer in Java
What are defaultdict in Python?
PL/SQL Explained
Directed Acyclic Graph: Representation
Thread Priority in Java: What is it & How to set?
Natural Join in DBMS SQL
Count Rows and Column with Pandas
10 Best Digital Campaigns that Inspired People
A Finance Expert's Views on Career Coaching (w/ Vaibhav Jain)
5 Most Important Google Ads Metrics
Top 50 DBMS Interview Questions and Answers 2023
Prim's Algorithm: Explanation, Code, and Applications
What is Immutable Class in Java?
ACID Properties in DBMS with examples
How to create an Empty Dataframe in Python using Pandas?
Java Bytecode
Functional and Non-Functional Requirements in Software Engineering
Generators in Python
Sales & Marketing Lessons from OYO’s Corporate Business Head (w/ Aditya Sharma)
3 Best Case Studies Of 2022 Influencer Marketing To Learn From!
How to Crack Full-Stack Interview at Amazon?
Working of Kruskal's Algorithm
Understanding the Difference between Rollback and Commit
Introduction to Static Keyword in JAVA
Learn about range() in Python
Hashtable in Java
Cohesion & Coupling in Software Engineering
Pandas append() in Python
Career Growth & Life Lessons from an Amazon Business Leader (w/ Manikantan Narayanan)
What are Big Brands up to? [Digital Marketing Updates]
How to Crack Capgemini Data Analyst Interview
A Quick Guide to Prototype Model in Software Engineering
How to sort a list in Java?
GroupBy Python Function & How To Use It!
NoSQL Databases: What are They?
Prims and Kruskal algorithm for Maximum Spanning Tree
Lambda Expression in Java
Python numpy.linspace()
4 Myths & Truths about Resume | What is Resume?
5 Year Career Journey from Business Analyst to Leading Data Science Team (w/ Geetanjali Prasad)
How to get a Digital Marketing Job at Capgemini?
Bellman Ford Algorithm in detail with code
Master Data Visualization using Python
Print Fibonacci Series in JAVA
Spiral Model in Software Engineering
Java Stream
Exit Command in Python
OLAP vs OLTP: Differences
Deep Dive into Software World with Software Development Engineer from Amazon (w/ Rahul Bhanushali)
Floyd-Warshall Algorithm and its Implementation
Understanding Anonymous Inner Class in JAVA
Star Schema and Snowflake Schema in Data Warehousing
Python Virtual Environment
LinkedList in Java
V Model in Software Engineering
Computer Science, Data Analytics, AI, and more with Mirza Rahim Baig (Analytics Lead at Flipkart)
25 BEST Software Development & Programming Tools in 2023
Understand Travelling Salesman Problem
Deep Understanding of Distributed Database in DBMS
Learn to Create an Array of Objects in Java
Python Socket Programming
Sorting A Hashmap In Java
AVP- HR of Manthan Systems enlightens about the field of Analytics
How to get Started with Freelancing as a Software Developer in 2023?
Types of Variables in Java
Deadlock in DBMS
Branch And Bound Algorithm: Explained
Finally Block In Java
What Brillio expects from an entry level talent pool in Analytics
Software Engineering Questions and Answers
How to Evaluate Postfix Expression
Learn about Java List
Trim in Java
Future Talent hiring Strategy
Introduction to Round-Robin Scheduling
Classes and Objects in Java
Talent Specialists - What do they look for?
Abstraction in Java
Disjoint set (Union find Algorithm)
Headhunting - A Challenge
State Space Reduction in Algorithms
Constructor Overloading in Java
What does a Martech company look for in Analytics?
Apriori Algorithm
Method Signature In Java
Data Science Lead - LinkedIn emphasizes the Skills of Analytics
What is A* Search Algorithm?
Method Overloading And Overriding In Java
Dive deep into eClerx's World of Analytics and Data Science
Introduction
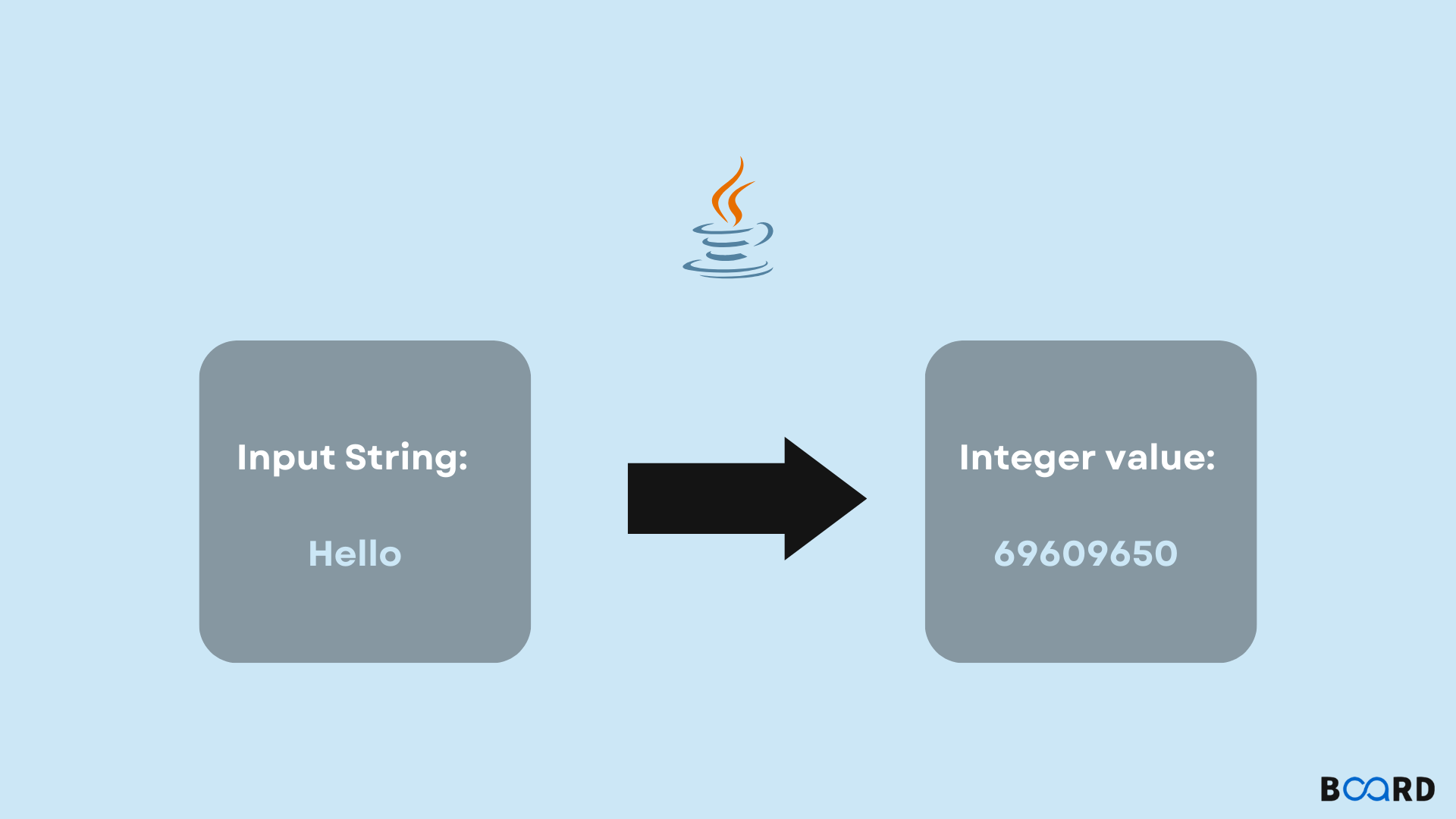
In computer science, hashing is a concept that involves mapping entities or objects to integer values. The values of those entities are called hashcodes or hash values.
In Java, to compute hash values of objects, the hashCode() method is used. In Java, the Integer class has two methods:
- hashCode(): It computes the hash values of the Integer.
- hashCode(int value): It computes the hash values of primitive int values.
Properties of Hashing
- When the output of the equals() method is the same as the object then they have the same hash value. That means they need to be mapped to the same Integer value.
- When two objects are not equal, they may or may not have the same hash values. That is why different objects do not need to have different hash values.
- When hash values of objects are computed multiple times, their hash values should remain consistent.
- When invoked more than once during the execution, the output of hashing algorithm must be the same for the same objects.
- But, from one execution to another execution the value does not need to stay consistent.
Java hashCode() Method
To compute the hash values of input objects, there is the hashCode() method in java. The value of that integer which represents the input object’s hash value, that integer is returned.
To produce the hash values of objects, the hashCode() method is used. These objects are then stored in Java collections such as HashMap, HashSet and HashTable by using these hash values.
In this example, we will see the properties of hashing by testing the following things:
Two objects having the same values also have the same hashcodes.
Objects that do not have the same values also don’t have the same hashcodes.
When the hashcodes of the same object are computed again, it gives the same hashcode or the hashcode is consistent.
Code
import java.io.*; |
Output:
HashCode of a1 = 100 is: 48625 |
Integer class hashCode(int value) Method
As can be seen clearly, this method computes the hash value of its parameter and return its hashcode.
Code
// Example of hashCode(int value) |
Output:
HashCode of value = 144 is : 144 |
